VirtualBox
comes with a set of command-line utilities, and you can use VirtualBox command-line interfaces (CLIs) to manage virtual machines on a headless remote server. In this tutorial, we will show you how to create and start a virtual machine without the VirtualBox GUI using VBoxManage. VBoxManage is the VirtualBox command line interface that you can use to fully control VirtualBox from the command line of your host operating system. VBoxManage supports all the features that the GUI gives you access to, but it supports much more than that. It really exposes all the features of the virtualization engine, even those that are not (yet) accessible from the GUI. You will need to use the command line if you want to use a different user interface than the main GUI and control some of the more advanced and experimental configuration options for a virtual machine.
VBoxManage will be useful when you want to create and run virtual machines (VMs) in VirtualBox, but only have access to a terminal on a remote host machine. This can be a common situation for servers where virtual machines are managed remotely.
Before
you start using the VBoxManage command-line utility, make sure that you have root or sudo user access to your Ubuntu 16.04 server and Oracle Virtual Box is already installed on it. Then, you need to install the VirtualBox Extension Pack, which is required to run a VRDE remote desktop server used to access headless virtual machines.
Installing VBoxManage You can get the required package by following the link to the Virtual Box download page to get the
latest extension pack, the same version as your installed version of VirtualBox!.
<img src="https://www.unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/12-1.png" alt=
“VBox Manage Extension” />
You can also use the following command to get the VBoxManage extension on your system
After downloading the package, you can install it on your system by flowing the command below.
Run the following command to confirm that VBoxManage has been successfully installed.
<img src="https://www.unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/21.png" alt="Check
VBoxManage” /> Using VBoxManage
in Ubuntu 16.04
Now let’s use VBoxManage to show you how easy it is that you can create and manage your virtual machines using this utility from the command line terminal. Let’s
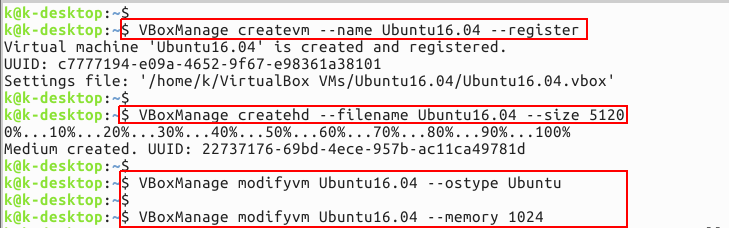
run the following command to create a virtual machine for Ubuntu OS.
After running this command, you will create a virtual machine named “Ubuntu16.vbox” in the home folder under “VirtualBox VMs/Ubuntu16/Ubuntu16.04.vbox”. In the above command, “createvm” is used to create a virtual machine and “-name” defines the name of the virtual machine, while the “registervm” command is used to register the virtual machine.
Now, create the hard disk image for the virtual machine by using the following command.
Here “createhd” is used to create a hard disk image
and “-filename” is used to specify the name of the virtual machine, for which the hard disk image is created. Here, “-size” denotes the size of the hard drive image. The size is always given in MB. Here we have specified 5Gb which is 5124MB.
Next, we will set the OS type, whether the Linux OS
needs to be installed, then specify the OS type like Linux or Ubuntu or Fedora, etc. using the following command.
Use the following command to set the memory size for the virtual operating system,
that is, the ram size for the virtual operating system from the host
machine.

Now let’s
create a storage driver for the virtual machine using the following command.
Here in the above command ‘storagectl’ is used to create a storage controller for the virtual machine, ‘-name’ specifies the name of the storage controller that needs to be created, modified or deleted from the virtual machine. Next, ‘-add’ defines the type of system bus to which the storage controller should be connected. Your available options are ide/sata/scsi/floppy. The ‘-controller’ option allows you to choose the type of chipset to be emulated for the given storage controller, while its available options are LsiLogic / LSILogicSAS / BusLogic / IntelAhci / PIIX3 / PIIX4 / ICH6 / I82078. In the end, ‘-bootable’ defines whether this driver is bootable or not.
The preceding command creates the storage controller named IDE. Later, the virtual media can be connected to the controller using the ‘storageattach’ command.
Now run the following command to create a storage controller called SATA, which will be used to attach the hard drive image to this later.
Connect the previously created disk image as well as the CD/DVD drive to the IDE driver. Ubuntu installation ISO image which is then inserted into the CD/DVD drive. Now, connect the storage controller to the VM using the ‘storageattach’ command.
This will connect the SATA storage driver to the Ubuntu16.04 virtual machine with the media, i.e. to the virtual disk image being created.
Run the following commands to add some features like network settings, audio, etc.
Now, start the virtual machine
by using the following command specifying the name of the virtual machine you want to start.
A new window will open where the new virtual machine will be started from the attachment.
To stop the virtual machine
, you can use the following command
.
The ‘controlvm’ command is used to monitor the state of the virtual machine. Some of the available options are pause/resume/reset/shutdown/savestate/acpipowerbutton/acpisleepbutton. There are many options in controlvm to see all the options available in it, run under the command.

Conclusion
In this article we have learned about an impressive Oracle Virtual Box tool that is VBoxManage, which includes its installation and use on Ubuntu 16.04 operating system. The article includes detailed instructions on your useful commands for creating and managing virtual machines using VBoxManage. I hope this will be of great help to you, do not forget to share your comments or suggestions.
If you like our articles, please use the “Get Linuxpitstop articles by email” option to get the latest articles by email. Please like, follow and share our social media pages, we need help from esteemed visitors like you to keep this company going.
