Random access memory or RAM in short, is a very important part of any computer. If you have purchased a new preconfigured Ubuntu computer or a virtual private server (VPS) and do not know any information about how much RAM you have, how much is used, the speed of the installed RAM, the type of RAM, then this article is for you. In this article, I will show you how to find information about your RAM or installed memory in Ubuntu 18.04 and also find out if you have any problems in your installed RAM. Start.
Checking RAM size and availability
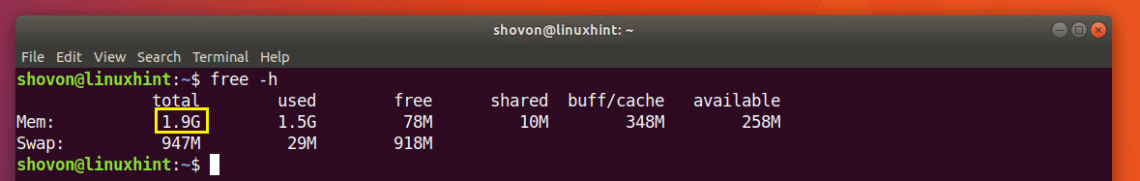
You can check how much RAM you have installed on your Ubuntu 18.04 machine using the following command:
As you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below, the total RAM installed on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is 1.9 Giga Bytes (GB).
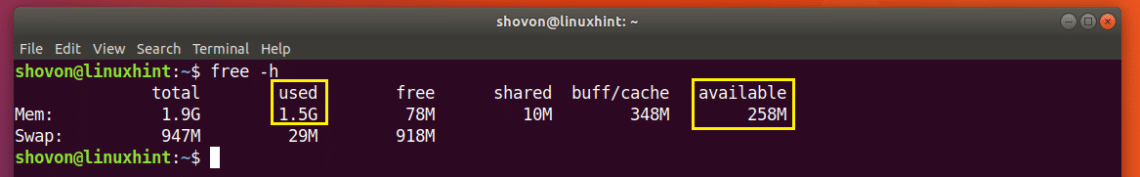
You can also find out how much RAM is used and
how much RAM
is available using the free command.
As you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below, the RAM used on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is 1.5 Giga Bytes (GB) and the available or free RAM is 258 Mega Bytes (MB).
Checking RAM type and speed
There are different types of RAM available in the market. For example, DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4. DDR here stands for double data rate. At the time of writing, the most commonly used type of RAM is DDR3 and DDR4. There are also other types of memory for portable devices, such as SDRAM, DRAM, etc.
Every RAM or memory module these days has different profiles. Each of these profiles defines the clock speed at which RAM should run.
You
can check the type of RAM you have installed on your Ubuntu 18.04 machine using the following command:

You should see the following window as shown in the screenshot below. This is a lot of information. You can press the <Up> and <Down> arrow keys to navigate through this information.
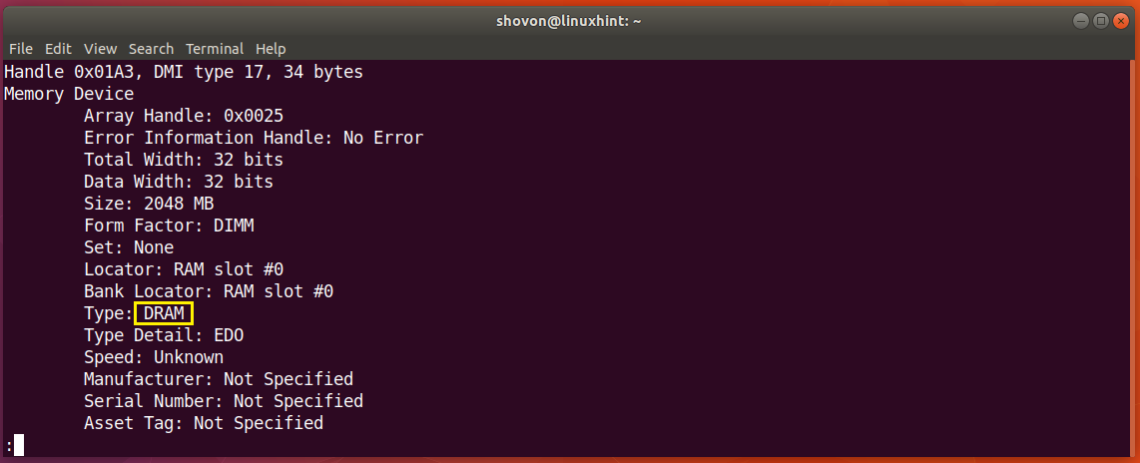
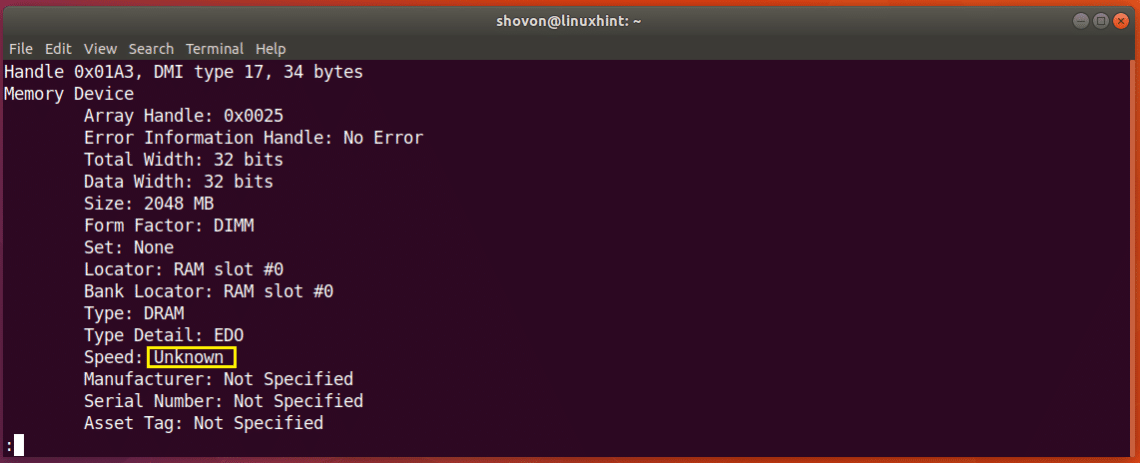
Just scroll down a bit and you should find information about your RAM. As you can see from the screenshot below, the type of RAM installed on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is DRAM.
You can also find out the clock speed or speed of the RAM installed on your machine using the dmidecode command. As you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below. I don’t have the speed of my RAM listed here since I’m using a virtual machine. But on real computers, it should be something like 1333 MHz or something.
Checking RAM errors
Sometimes, your RAM can suffer from a lot of problems, as semiconductor devices like RAM are very fragile. You can check your RAM for errors.
In Ubuntu 18.04, you can use the memtester command-line utility to check for errors in your RAM. memtester is not installed on Ubuntu 18.04 by default. But it is available in the official Ubuntu 18.04 package repository.
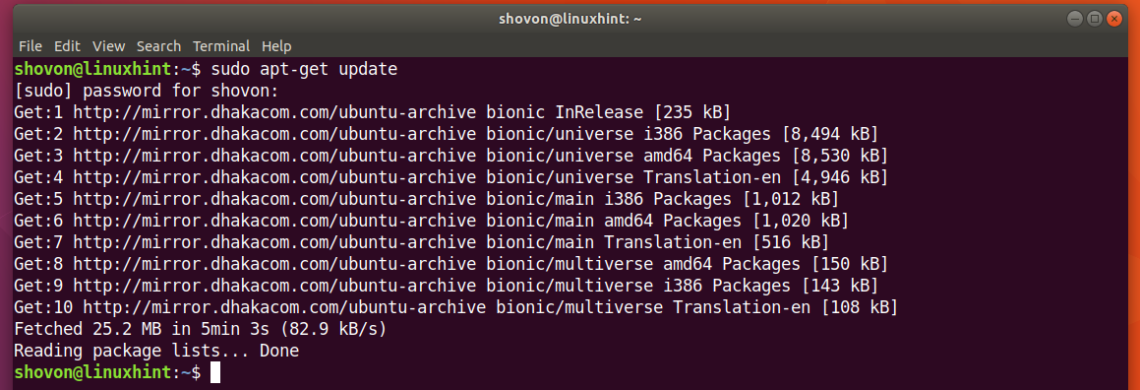
First refresh the package repository cache of your Ubuntu 18.04 machine with the following command: 
The package repository cache needs to be refreshed
. 
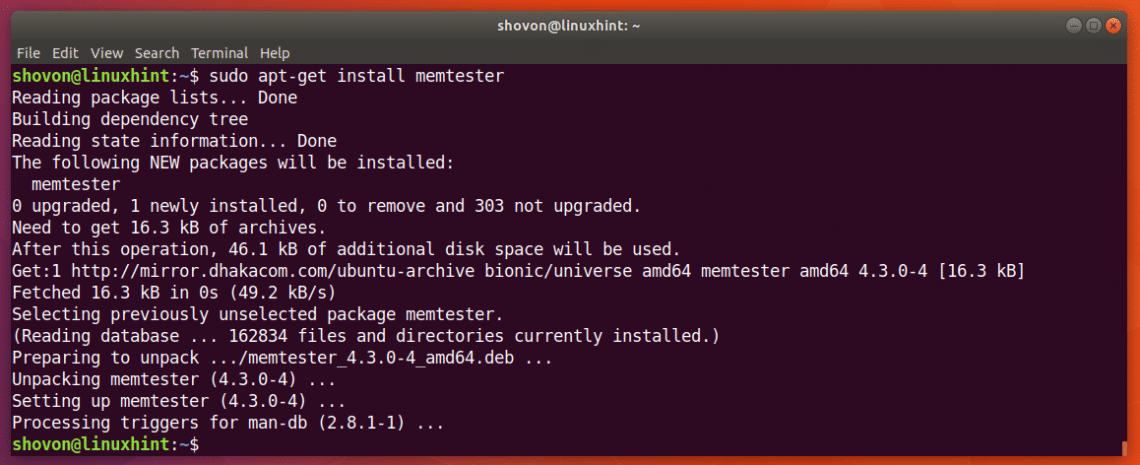
You can now install memtester on Ubuntu 18.04 with the following command:
<img
src=”https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/r9.png”
alt=”” />
memtester should be installed.
You can now run the memtester command to check the memory as follows: Here SIZE is the amount of memory to allocate and test using the
memtester
utility.
ITERATIONS is a number that specifies how many times you want memtester to test allocated memory.
As SIZE you can use B for Bytes, K for Kilobytes, M for Megabytes and G for Gigabytes.
Let’s say you can allocate 100 Megabytes in RAM and double check. You can run the following command to do so:

As you can see in the screenshot below, the memtester program is testing the RAM. 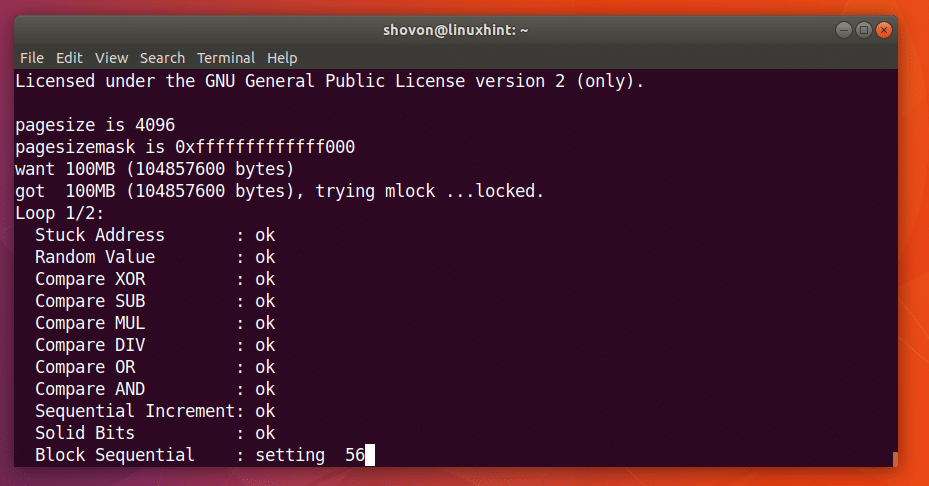 When memtester
When memtester
command is complete, as you can see in the screenshot below, all tests are successful. It means that the RAM has no errors. Of course, you can allocate more memory at once for a thorough test.
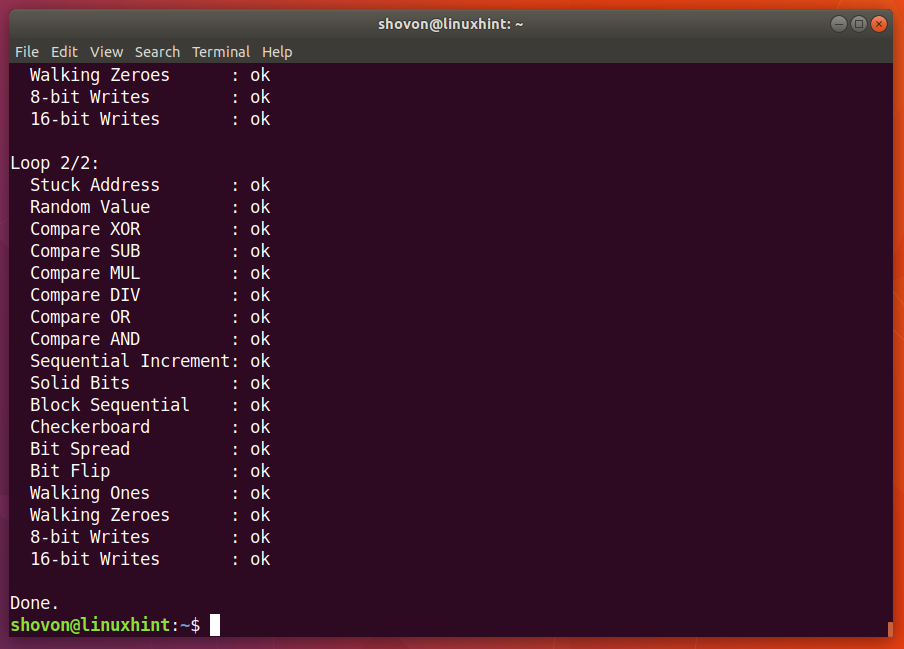
The only drawback of the memtester utility is that you cannot allocate more RAM than you have available as free
.
You can use memtest86+ to do a more thorough check of your RAM. It has no limitations as memtester. It is installed by default on Ubuntu 18.04.
Simply restart your Ubuntu machine and from the GRUB menu, select Memory Test (memtest86+).
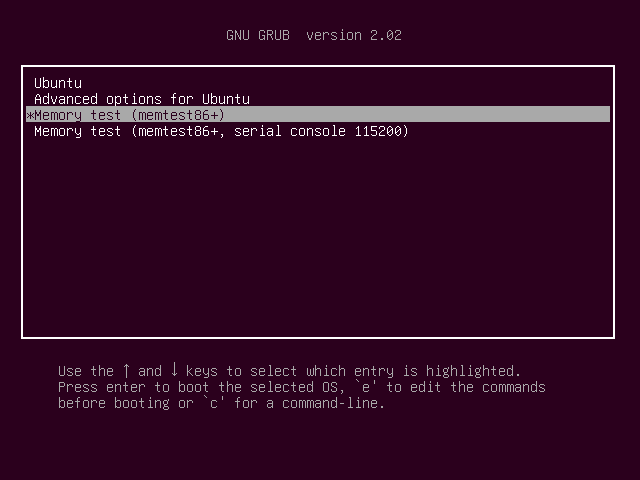
You should see the following window. Now press F1 to go to safe mode.

memtest86+ should start checking your RAM for errors, as you can see in the screenshot below
.
<img src="https://linuxhint.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/r16.png" alt=
“
” />
This is how you discover different information about RAM and check RAM for errors in Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver. Thank you for reading this article.
