Setting up the network and bringing servers to the network is the
primary administration task for any system administrator
.
In some cases, these tasks are automated by DHCP (Dynamic Network Configuration Protocol) which is responsible for assigning the IP address to the desktops/servers.
READ: How to set up DHCP server on CentOS 7,
Ubuntu 18.04 and Debian 9
But, if you go to larger organizations, they use static (manual) IP to avoid network problems due to unavailability of DHCP servers
.
Configure Static IP Address on CentOS 7/RHEL 7
Let’s configure our system for the following information
. IP address: 192.168.1.10 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Gateway (router): 192.168.1.1 DNS server 1:
192.168.1.1DNS Server 2: 8.8.8.8Domain name: itzgeek.local
Find available network interfaces at
Your system You can use any of the following commands to list the network interfaces available on your system.
ifconfig -a
or
IP a
Choose the
desired network interface
The output of ifconfig -a can be seen as shown below. Here, I want to change the IP address of enp0s3.
ENP0S3: FLAGS=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> MTU 1500 INET 192.168.1.7 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 inet6 fd50:1d9:9fe3:1400:a00:27ff:fe98:676 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0 inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe98:676 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20 ether 08:00:27:98:06:76 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 2997 bytes 3497708 (3.3 MiB) RX errors 0 removed 0 overflows 0 frame 0 TX packets 1487 bytes 135487 (132.3 KiB) TX errors 0 removed 0 overflows 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> MTU 65536 INET 127.0.0.1 Netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10 loop txqueuelen 0 (local loopback) RX Packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX 0 errors discarded 0 overflows 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX Errors 0 Deleted 0 Overflows 0 Carrier 0
Collisions 0 Configure the static IP address
Method 1
In this method, we will edit the network interface file that is located in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. For the enp0s3 interface, the file name would be ifcfg-enp0s3.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
Update the interface file as required.
HWADDR=08:00:27:98:06:76 TYPE=Ethernet # Static IP Address # BOOTPROTO=none # Server IP # IPADDR=192.168.1.10 # Netmask # NETMASK=255.255.255.0 # Default gateway IP # GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 # DNS servers # DNS1=192.168.1.1 DNS2=8.8.8.8 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no # Disable ipv6 # IPV6INIT=no # Device Name # NAME=enp0s3 DEVICE=enp0s3 # Optional – This is system specific and can be created using the command ‘uuidgen enp0s3’ # UUID = 02d4a47b-3dbe-4e0b-ae4b-841a8c58e807 # Activate at boot # ONBOOT = yes # Default domain search # DOMAIN=itzgeek.local
Method 2
You can also use nmtui, a text-based user interface for configuring network interfaces. nmtui
Select Edit a connection and press Enter.
<img src="https://www.itzgeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Configure-Static-IP-Address-in-CentOS-7-Edit-a-connection.png" alt="Configure static IP address on CentOS 7 – Edit a connection
Choose the network interface, and then choose Edit.
 Configure static IP address
Configure static IP addressSet the IP address and enter OK.
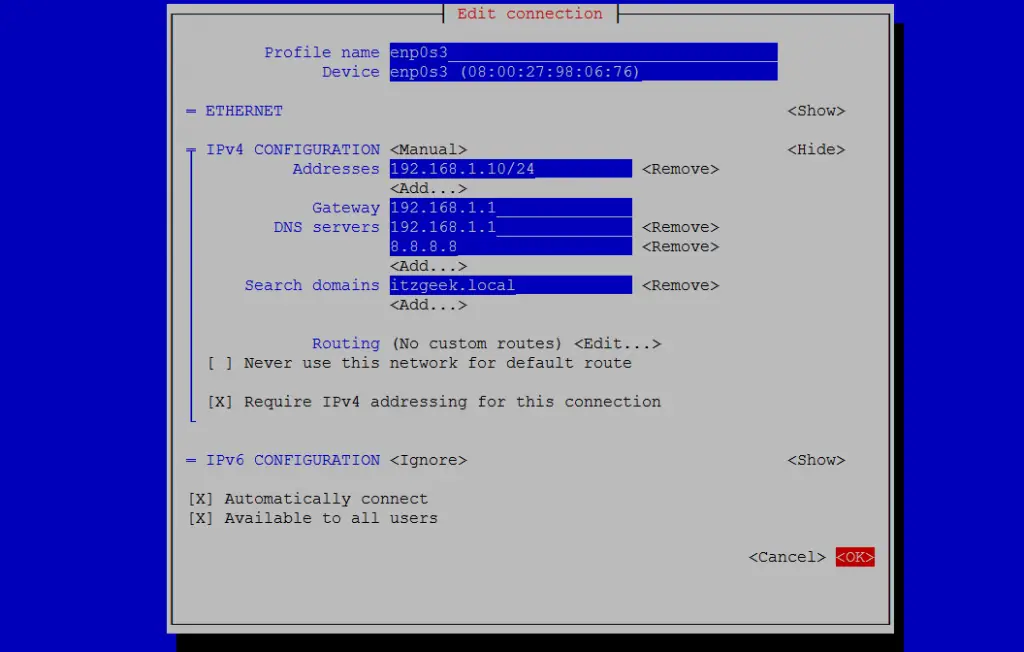 Configure Static IP Address
Configure Static IP AddressRestart
Network
Finally, restart the network service by using the following command for these changes to take effect.
Restarting systemctl network
Verify
static IP address
Use the ifconfig -a command to verify the static IP address
. ENP0S3: FLAGS=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> MTU 1500 inet 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 inet6 FD50:1D9:9FE3:1400:A00:27FF:FE98:676 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0 inet6 fe80::A00:27FF:FE98:676 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20 ether 08:00:27:98:06:76 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 55 bytes 6637 (6.4 KiB) RX errors 0 deleted 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 84 bytes 12745 (12.4 KiB) TX errors 0 deleted 0 overflows 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> MTU 65536 INET 127.0.0.1 Netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10 loop txqueuelen 0 (local loopback) RX Packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX 0 errors removed 0 overflows 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 deleted 0 overflows 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
In addition, verify the DNS server entries
. cat /etc/resolv.conf
Output:
# Generated by NetworkManager search itzgeek.local nameserver 192.168.1.1
nameserver
8.8.8.8 Conclusion
That’s it. I hope you learned how to set up a static IP address on CentOS 7/RHEL 7.
